The importance of heart rate zones for health and performance

Are you looking to take your heart rate zone training to the next level?
If so, metabolic testing may be the answer.
Metabolic testing can help you optimize your exercise routine by providing information on how your body uses energy.
This information will help you:
- fine-tune your training and
- improve your performance and
- learn so much more about your heart rate zones!
Let’s explore what Pnoe metabolic testing is and how it can help you achieve your fitness goals.
Keep reading to learn more!
Here is what you will learn in the post about heart rate zones and what it means for you!
Table of Contents
- What are heart rate zones?
- What’s our body’s fuel mix, and how does it help determine training zones?
- How many training zones do we use? What physiological traits does each one train?
- Zone 1
- Zone 2
- Zone 3
- Zone 4
- Zone 5
- Why should I care about training zones?
What is Heart Rate Zones all about and is this for me?

You’ve probably heard about heart rate zones?
Elite endurance athletes and a growing number of recreational athletes use them to guide their workouts.
How you can use this data to help you change your body and training?
How can you get the most out of your body?
Let’s get into the basics.
What are heart rate zones?
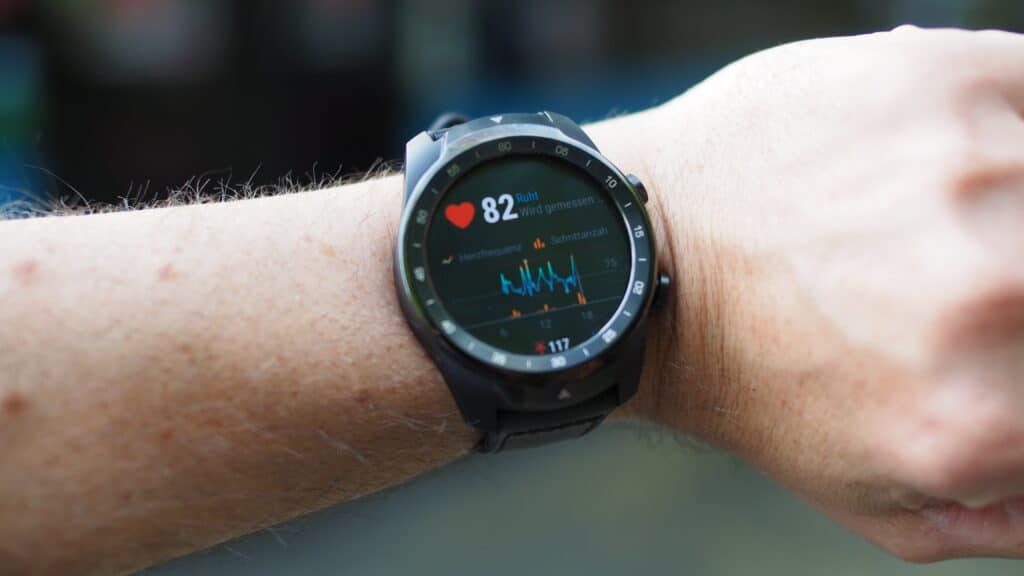

Heart rate training zones reflect your body’s metabolic statuses in different training intensities.
They are heart rate ranges (e.g., 123 – 142 beats per minute), each one corresponding to an exercise intensity, where your body responds metabolically in a specific way.
Two factors determine the metabolic state of your body in each zones:
The Two Heart Rate Zone Factors
- The fuel mixture used (i.e., the balance between fats and carbohydrates).
- The physical traits your body develops when training in this zone.
For example, when training in heart rate zone 2, your body will burn the most fat and enhance its cellular health fat-burning capabilities at the fastest rate.
During exercise, your body typically burns a mixture of fats and carbohydrates to release the energy required (i.e., calories) to move.
Fat releases more energy than carbs when burnt (i.e., 9 kcal per gram of fat vs. 4 kcal per gram of carbs) but has a slower burning process making it suitable for low exercise intensities where the rate of energy demand is low.
Carbs to burn
Carbohydrates, on the contrary, require less time to burn and can therefore support higher exercise intensities where the rate of energy demand is larger.
The breakdown of oxygen and carbon dioxide in your breath, as well as the use of a metabolic analyzer like Pnoe, gives you an indication of your body’s composition by way of a gas law.
Figure 1 shows the difference between fat and carbohydrate burn as exercise intensity increases during a treadmill test.
Figure 1 Dark green: fats, Turquoise: carbohydrates, Light green: heart rate
How Data Is Collected

Since this measurement requires you to wear a mask, information about your body’s fuel usage becomes almost impossible to obtain during everyday training.
As a result, we use heart rate as a proxy metric to accurately estimate our body’s fuel usage and metabolic status.
This is done via a metabolic test. It involves monitoring heart rate and the proportion of fat, carbohydrates, and protein in your bloodstreams.
Taking Heart Rate Zones Personal
We refer to this as “getting your personalized training zones”.
However, it’s important to note that the correlation between heart rate and fat-carbohydrate balance depends largely on the type of exercise.
For example, you may be burning 30% fats and 70% carbs at 140 beats per minute when running but only 15% fats and 85% carbs at 140 beats per minute when cycling.
How many Heart Rate zones do we use? What physiological traits does each one train?
The breakdown of oxygen and carbon dioxide in your breath, as well as the use of a metabolic analyzer like Pnoe, gives you an indication of your body’s composition by way of a gas law.
Zone 1

Zone 1 in primarily warmup. This means that you are recovering from a previous workout while still moving.
Zone 2

Zone 2 training will develop your mitochondrial function and improve your fat-burning efficiency.
It’s perfect for long-distance endurance sports and those with metabolic syndrome.
The improved mitochondrial function will also significantly support recovery capacity helping you to recover faster after intense bouts of exercise.
Zone 3

Zone 3 training can help strengthen your pulmonary muscles and improve cardiovascular function.
It’s an ideal intensity when suffering from a lung or heart problem since its moderate- intensity offers a strong stimulus to the heart and lungs without being exhausting or overly strenuous.
Zone 4

Image by Fernando Latorre from Pixabay
Zone 4 training will help improve your VO2max and ability to sustain high-intensity exercise for prolonged durations by improving lactate shuttling.
Lactate is produced in your muscles during anaerobic exercise.
This also consume as energy.
As long as your body can get rid of the fatigue byproducts faster than they are produced, you can keep exercising at the same intensity.
As a result, the greater your lactate shuttling capability the greater your ability to sustain high exercise intensities for long periods of time.
Zone 5

Image by Dave Noonan from Pixabay
Zone 5 training will improve your VO2max and peak power output capability (e.g. maximum speed or cycling wattage).
This exercise intensity is sustainable for 60 to 120 seconds and requires one to train at his maximum potential.
Why should I care about Heart Rate zones?

Regardless of age, gender, and fitness level, every person has one or more systems posing a limitation to fitness or health.
Targeting these limitations effectively requires the precision that stems from focusing your cardio and interval training in the zone(s) that will bring about the adaptations needed to overcome them.
The PNOE metabolic analyzer provides gold-standard accuracy in determining your training zones along with the plan that puts them to effective use.

Understanding how your body responds metabolically differently and building your program around your metabolism is a foundational step toward maximizing your workout’s efficiency and achieving your health or performance goals faster and with less effort.
Conclusion
Now that you know what heart rate zones are, it’s time to put this knowledge into practice.
Check out the different training zone options we offer and find the best one for your needs.
After all, knowing is only half the battle – you have to take steps to improve your fitness level and achieve your goals!
By the way, on behalf of myself and my small team of creators want to take a moment to sincerely thank you for reading this post as my aim is to always provide solutions, not problems, and life people higher not lower in life!
Bottom line: I am only here to IMPROVE the quality of life for all that allow me!
If you want to contact me directly, then let’s get you booked on my calendar!
Other Content You May Be Interested In
- Should women over 40 take CoQ10? Vital Benefits and Insights
- Power Plate Exercises For Arthritis: A 2024 Comprehensive Guide
- Knee-Friendly Fitness: Debunking Myths About Vibration Plates and Knee Health in 2024
- 5 Delicious Ways to Celebrate National Pistachio Day (and Reap the Health Benefits!) 2024
- Where Would Bay Leaves Be In a Grocery Store?-This Awesome Frugal Guide Brings Clarity For 2024

I am extremely inspired to make a positive
IMPACT in the world by helping you create FREEDOM.
INSPIRE you to believe in yourself and achieve more of what you want for yourself…
And of course, I am here to help you IMPROVE your quality of life!
Book some time on my calendar if you want to connect directly to me!

